The Australian dollar has fallen to its lowest level in 10 years. The price of the Australian dollar is simply driven by demand and supply. Price goes down when the demand is low and price goes up when demand goes up. So why has demand been falling for Australian dollars?
Interest Rates
The US cash rate is 2.5% and Australian interest rates are only 1% at the moment. The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is considering further interest rate cuts.
Currency investors will consider the country with the highest interest rates as the better option to invest in. With the interest differential between the Australian and US market, the higher interest rates in the US will drive up demand for US dollars, and therefore less demand for Australian dollars.
Volatile Times
The US dollar is considered a safe haven during tumultuous economic times so the popularity of the dollar is increased during these periods.
US treasury bonds are considered a safe investment as they have never defaulted on payments to investors. Hence these instruments are considered safe havens during uncertain times. As the demand for US bonds increases so does the US currency rate. Investors need to pay for these US bonds in USD so they need to sell out of their foreign currency and pay in USD dollars and this drives the US dollar value up.
Global Growth is Going Down
Australia’s top exports are heavily weighted in commodities. This means as global growth slows, so will the demand for Australian commodities., Australia’s top export is iron ore which is a key ingredient in making steel. Demand for steel has been decreasing as growth globally has slowed. Slowdown for demand of iron ore therefore weakens the strength of the Australian dollar.
As Australia is such a big exporter, when iron ore prices fall, the income generated from this sector decreases the total income flowing into the Australian economy. This can decrease foreign capital inflows which can cause the Australian dollar to fall. When iron ore demand increases, so does the flow of foreign capital. Importers purchasing Australian commodities need to convert foreign currency into Australian dollars. So, an increase in demand for iron ore then causes a higher AUD currency.
See below the chart below which shows the percent change of the AUD/USD dollar against the annual percentage change of the Global Price Index of all Commodities. The chart shows there is a link between the two.
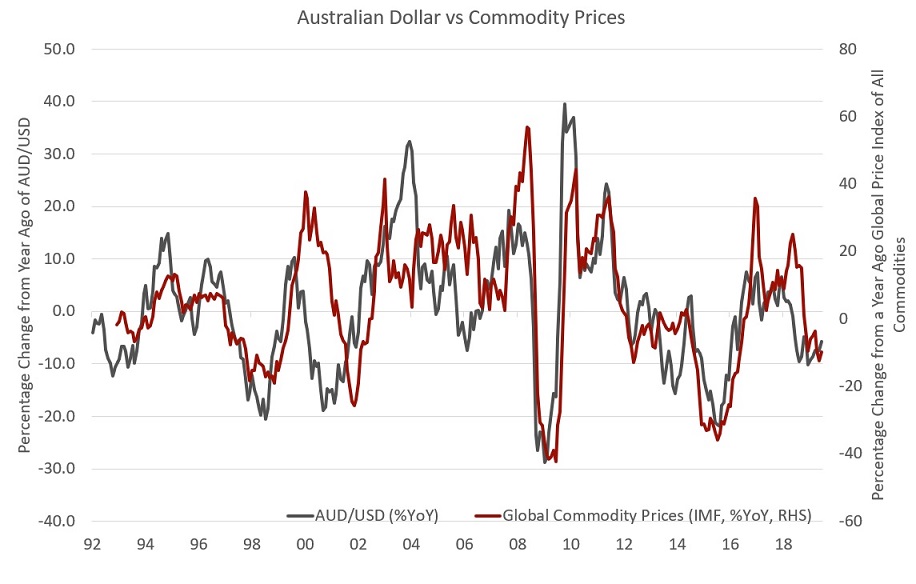
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis
China’s economy
Australian’s largest trading partner is China as we export 29.2% of total Australian exports to this country. Therefore the Australian currency is significantly impacted by a fluctuation in the Chinese yuan. When the Chinese yuan falls, the Australian dollar follows. The Chinese currency has been volatile lately. This is mainly as the result of the ongoing trade wars with the US.
Lauren Hua is a private client adviser at Fairmont Equities.
An 8-week FREE TRIAL to The Dynamic Investor can be found HERE.
Would you like us to call you when we have a great idea? Check out our services.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is general advice only. Read our full disclaimer HERE.
Like this article? Share it now on Facebook and Twitter!

